How to Install Tomcat on Linux?
Now that we understand what Tomcat does, and have covered the prerequisites, it is time to install Tomcat on our system. To do so, you need to follow the following steps.
Setting up a Tomcat User
It is not advisable to run Tomcat under a root account. Hence we need to create a new user where we run the Tomcat server on our system. We will use the following command to create our new user.
sudo useradd -r -m -U -d /opt/tomcat -s /bin/false tomcat
Copy
As you can see, we grouped our new system user with the directory /opt/Tomcat. This will be used to run the Tomcat service on our system.
Downloading the Tomcat package
Now that we have created a new user for our Tomcat server and switched to it. We need to download the Tomcat package to install Tomcat on Linux.
Let’s use the wget command to download the Tomcat package from their official website.
wget -c https://downloads.apache.org/tomcat/tomcat-9/v9.0.34/bin/apache-tomcat-9.0.34.tar.gz
Copy
Install Tomcat on Linux
Once the tar archive is downloaded on our system, we need to untar the archive on our system. This can be done as follows using the tar command as shown below.
sudo tar xf apache-tomcat-9.0.34.tar.gz -C /opt/tomcat
Copy
Using this command, we have extracted the contents of the tar package in /opt/Tomcat. To make updating Tomcat easy, we create a symbolic link that will point to the installation directory of Tomcat.
sudo ln -s /opt/tomcat/apache-tomcat-9.0.34 /opt/tomcat/updated
Copy
Now, if you wish to install Tomcat on Linux with a newer version in future, simply unpack the new archive and change the symbolic link so that it points to the new version.
Now we need to provide the user Tomcat with access for the Tomcat installation directory. We would use the chown command to change the directory ownership.
sudo chown -R tomcat: /opt/tomcat/*
Copy
Finally, we will use the chmod command to provide all executable flags to all scripts within the bin directory.
sudo sh -c 'chmod +x /opt/tomcat/updated/bin/*.sh'
Copy
Don’t forget to make sure that the “tomcat” user and group has read and write access to all the files and folders within the /opt/tomcat/updated folder like below.

See how both the user and group for the directories is tomcat and tomcat.
Configuring the Tomcat service
Once you install Tomcat on Linux, you need to configure it before you can start using it. First, we need to create a systemd unit file to be able to run Tomcat as a service. We need to create a new unit file for this. We will open a new file named tomcat.service in the directory /etc/systemd/system using nano or your preferred editor.
sudo nano /etc/systemd/system/tomcat.service
Copy
Now enter the following in your file and save it. Note that you need to update the value of JAVA_HOME if your Java installation directory is not the same as given below.
[Unit]
Description=Apache Tomcat Web Application Container
After=network.target
[Service]
Type=forking
Environment="JAVA_HOME=/usr/lib/jvm/java-1.11.0-openjdk-amd64"
Environment="CATALINA_PID=/opt/tomcat/updated/temp/tomcat.pid"
Environment="CATALINA_HOME=/opt/tomcat/updated/"
Environment="CATALINA_BASE=/opt/tomcat/updated/"
Environment="CATALINA_OPTS=-Xms512M -Xmx1024M -server -XX:+UseParallelGC"
Environment="JAVA_OPTS=-Djava.awt.headless=true -Djava.security.egd=file:/dev/./urandom"
ExecStart=/opt/tomcat/updated/bin/startup.sh
ExecStop=/opt/tomcat/updated/bin/shutdown.sh
User=tomcat
Group=tomcat
UMask=0007
RestartSec=10
Restart=always
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
Copy
Now we reload the daemon to update the system about the new file.
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
Copy
We use the following command to start the Tomcat service on our system.
sudo systemctl start tomcat
Copy
We will use the systemctl command to check the status of our Tomcat service. If the output looks like this, you were successful to install Tomcat on Linux.

Now we can enable the Tomcat service to run on startup using this command.
sudo systemctl enable tomcat
Copy
After you install Tomcat on Linux, you need to allow it to use the 8080 port through the firewall to be able to communicate outside your local network.
sudo ufw allow 8080/tcp
Copy

Verifying our installation
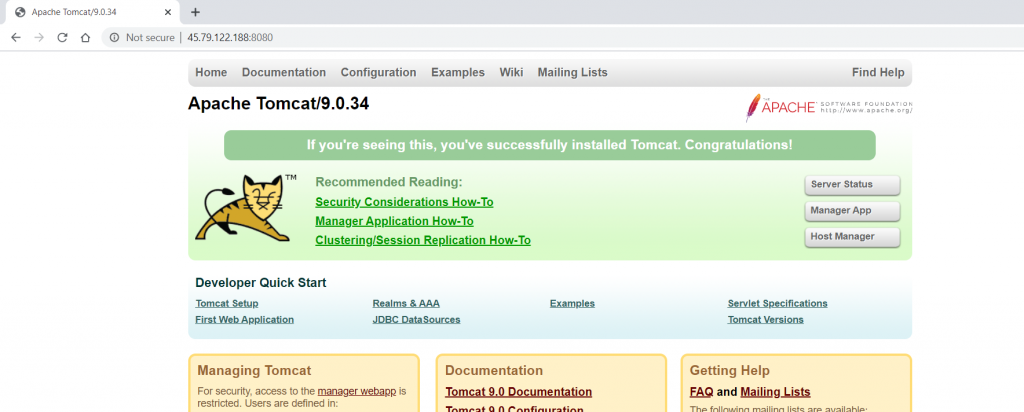
Once we install Tomcat on Linux, we need to verify our installation. To do so, simply enter the following in your browser.
http://<YourIPAddress>:8080
Copy
If your installation and configuration were successful, you should see this page.
