When configuring remote servers with Ansible, you may encounter instances where you need to get files from a Git repository. This could be a software package from public repositories or configuration files on a private repository.
To clone a git repository remotely using Ansible, you may add entries like this to your Playbook.
---
- hosts: all
tasks:
- name: Clone a github repository
git:
repo: https://github.com/sqlite/sqlite.git
dest: /home/debian/repos/
clone: yes
update: yesDon’t worry. I’ll explain what those parameters mean and how to do it with an Ansible git clone example tutorial.
Cloning Git repositories with Ansible
I presume you are already familiar with Ansible basics like inventory, playbooks etc. If not, you may follow our Ansible tutorial series.
Prerequisite
You must have Ansible installed on your local machine. This Ansible instance acts as the control node for all remote hosts. Using the control node, you can create playbooks and tasks to execute on the specified remote machines.
If you choose to follow this tutorial, ensure you have:
- One control node and one remote host.
- SSH key pairs. The public key of control node must be available in the authorized_keys file in the remote hosts.
- A non-root user with
sudoprivileges on the remote hosts. - Write access to a directory on the remote host to store the contents of the cloned repo.
Set up Ansible Inventory
Before proceeding further, you need to set up the Ansible inventory. The Ansible inventory is a file that contains information about the remote servers you wish to manage with Ansible.
By default, the file is located in /etc/ansible/hosts. Create this file manually if it does not exit.
Add the IP address of the remote host in this file:
vim /etc/ansible/hosts
It could look like this:
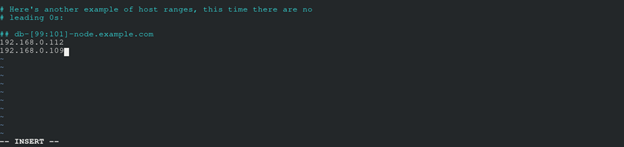
Save the file.
Cloning a Git Repository with Ansible playbook
Now that you have the inventory file configured and SSH keys in place to access the remote hosts from the control node, you can create the Ansible Playbook.
Using a text editor like Vim and create a YAML file.
vim clone.yaml
Edit the file and add the following entries.
---
- hosts: all
tasks:
- name: Clone a github repository
git:
repo: https://github.com/sqlite/sqlite.git
dest: /home/debian/repos/
clone: yes
update: yes
In the playbook above, you started by defining a new task and gave it the name “Clone a GitHub repository”.
Next, you use the git module to specify the link to the SQLite GitHub repository.
You then proceed to define the destination for the cloned repository. This is a local directory in the remote machine.
You set the attribute clone to yes to clone the repository and update it using the update attribute.
To run the playbook, use the command:
ansible-playbook clone.yaml
If the playbook fails due to SSH authentication, you can specify the username using the -u flag as:
ansible-playbook -u debian clone.yaml
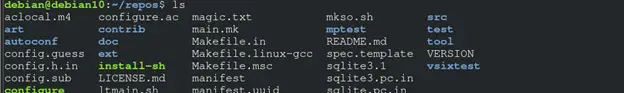
Once the tasks have been executed, you should have the repository cloned in the specified directory.
You can log in to the remote host to verify that the repository was cloned properly: